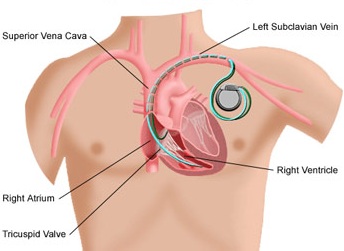
What is a pacemaker? |
A pacemaker is a small, implantable, electronic device that detects the electrical activity of the heart through special leads and provides pacing of certain heart chambers in
the form of electrical impulses in case of severe bradycardia (Slow heart beat) The implantation of such a device is indicated in specific cases to prevent episodes of fainting that are caused by a slow heart rate, and it is performed using local anaesthesia, usually in the upper left chest. A pacemaker has also the ability to synchronise the heart chambers (atria and ventricles) for more efficient heart function. After implantation, the pacemaker function is monitored regularly with special equipment and over time it might need to be replaced as the average generator (battery) life is about eight years. The procedure to replace the generator is simple and safe. There are many types of pacemakers with different indications depending on the case. The key difference is the number of heart chambers that need to be paced and the requirement for defibrillation capability in specific patient cases. |